This page is limited to our registered members
-
Get access to exclusive dermatological services to increase your professionnal knowledge: +500 pathology visuals, clinical cases, expert videos
-
Benefit from valuable features: audio listening, materials to be shared with your patients
-
Stay informed about the upcoming events and webinars, latest scientific publications and product innovations
Already have an account? login now
BIODERMA Congress Reports EHSF 2022
Report written by Dr. Nicolas Kluger (Dermatologist, Finland)
Related topics
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a challenging by its nature disease (Figure 1).
Figure 1: The challenges of HS
The 11th European HS Foundation conference took place from the 9th to the 11th of February. The information about the foundation can be found on www.ehsf.eu.
Report written by Dr. Nicolas Kluger
T Tzellos. Which comorbidities should I take into consideration. Symposium 02b-01
T Tzellos from Trömsoe reminded the high burden of the comorbidities associated with HS (table 1). HS is associated with a wide range of organic and psychiatric comorbidities. Screening and optimizing treatment strategies according to evidence is essential. A multidisciplinary approach is warranted.
Table 1. Comorbidites associated with HS (non-exhaustive list)
Report written by Dr. Nicolas Kluger
HS occurs usually between 20 and 30 years of age. However, HS in paediatric population is less known. It may be associated with a family history and a female predominance and possibly a more severe disease. Detecting HS in paediatric population is also of importance as HS is a life-long disease and delay in diagnosis and management may lead to worse outcomes and a high risk of cumulative life course impairment.
F. Prignano, et al. Clinical characterization of paediatric-onset hidradenitis suppurativa: results from a multicenter European study. S01-01
A retrospective multicentric international study reviewed a series of 56 teenagers (age 16 years-old, 28 girls) with HS. Age at onset ranged from 5 to 18 years-old, but almost half of the cases started at the age of ≥14. The diagnostic delay was rather short (1 to 2 years) compared to what is observed in adults. Less than 50% of the patients had comorbidities, including overweight/obesity. Boys tended to have a later age of onset and a history of acne and pilonidal sinus. BMI or tobacco smoking are not different between genders. A median of three sites were affected at presentation, mainly axillary, inguinal and genital areas. The genital area was more likely to be affected in case of early onset (before the age of 14 yo). Longer diagnostic delay was higher number of sites, higher severity scores and higher BMI.
M. Delage-Toriel, et al. Pediatric population in the Institut Pasteur Hidradenitis Suppurativa patient group : characteristics and evolution after antibiotic treatment
M Delage from the Institut Pasteur in Paris, France, presented their experience from 91 children and teenagers <18 yo. The median age at onset was 12 y (3-17) with median age at diagnosis of 14 yo. There was a female predominance (69%) and 55% of the cohort was overweighted or obese. Hurley stage were as follows I, 60% ; II 26% and III 13%.
Besides, 40% had on comorbidity or more, polycystic ovaries syndrome for girls (14%). In their series antibiotherapy lead to improvement and/or remission in more than 80% of their patients.
The antibiotherapy used in Institut Pasteur is summarized in Figure 2:
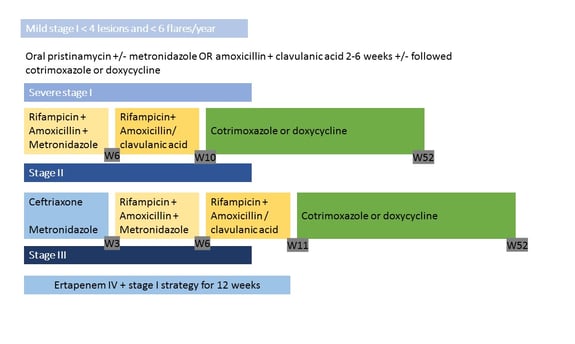
Antibiotherapy protocols for children with HS as given at Institut Pasteur
Report written by Dr. Nicolas Kluger
F Ohm, et al. Prevalence of inflammatory bowel diseases in hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa population – results from the German Hidradenitis-Suppurativa-Registry HS- BEST. S01-03
The aim of the study was to evaluate the prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome in a cohort of patients from a German web-based registry HS- Best. The data are based on the self-report of the patients in the database. Among the 342 patients that were extracted, 0.9% reported ulcerative colitis, 2.6% Crohn’s disease and 5.6% irritable bowel syndrome. Patients with IBD were older than those without and there was a female predominance among the patients reported intestinal symptoms. It is however important to remind that the study is based on the reports of the patients and all the patients were based in Hambourg and are not representative of the whole registry.
Report written by Dr. Nicolas Kluger
K. Bouwman, et al. Dietary intake and physical activity of hidradenitis suppurativa patients in a large population-based cohort. S01-06.
A Dutch case-control study has investigated the nutritional intake and physical activity of HS patients compared to the general population. It was studied within a large prospective study that included more than 160 000 residents of Nothern Netherlands (Lifelines study, 10% of the population in the Netherlands). From this cohort, 5440 individuals were included: 1 004 HS patients compared to 4 436 age matched controls randomly selected. A self-administrated questionnaire allowed to evaluate the individual intake over the previous month (food frequency questionnaire, that included 110 food items divided in 25 food groups) and to calculate the intake of food items in grams/day. From this, a diet score from 0 to 48 (healthier diet) was calculated. Besides, physical activity has been also evaluated.
In the HS group, 70% of the patients had a Hurley I score and a third was smoking. The group had a higher BMI than controls (26.4 vs 25.3). HS patients ate less whole grain products, less vegetables and nuts, less fruits, less fish, less dairy products, less sugar products but more artificially sweetened products and savory/ready products. The diet score was significantly lower in HS patients. The physical activity was also diminished in the HS group.
Dietary and physical activity habits are different between patients and controls. Healthier lifestyle could play a role in the management of HS.
Report written by Dr. Nicolas Kluger
J. Romani et al. Dapsone in HS: why, who, when and how
Dapson is an know antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs used in dermatology and in HS disease. Dapsone is usually suggested as second or third lines of therapies according to national guidelines. However, there is no randomized controlled trials that have include dapsone in HS. A monocentric retrospective study from Spain evaluated the efficacy of dapsone in a cohort of 56 patients with HS. The patients were mainly male (66%), smokers (62%), with acne (55%) and pilonidal sinus (14%). More than half of the patients were Hurley I stage. Regarding phenotype, 69% had a LC2 (follicular), 20% LC3 (gluteal) and 11% LC11 (regular axillar-mammary). At 3 months, 63% displayed a response to dapone (50-150 mg/day). Mean duration of treatment was 8 months and 4 responders received also acitretin in association. The best response was seen with patients with Hurley I stages, on patients with LC2 and LC3 phenotypes in case of pustular/nodular lesions. On the other side, patients with sinus tracts responded less well. Treatment was well tolerated in general.
Report written by Dr. Nicolas Kluger
B. Horvath, et al Impact of COVID-19 on Hidradenitis Suppurativa Patients. P068
In a large study from the Netherlands comparing more than a thousand of patients with HS and 4600 controls, the prevalent of COVID-19 was similar between both groups (5.7 vs 5.2%). HS patients reported more side effects after vaccination (51.3 vs 39.6%) he proportion of patients that had received one shot of vaccination was also similar.
Precautions taken to prevent infection (washing hands, social distancing, covering mouth and nose in public, avoiding public transport) were comparable. However, patients with HS acknowledged a greater impact on their quality of life, more concerns about the pandemic and fear for getting sick.
J. Kopytev et al. Incidence of COVID-19 hospitalization in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa
A retrospective American study showed that during the year 2020 the incidence of COVID-19 hospitalization for 33 for 10 000 HS patients among patients under biologics, 143 among those with other treatments and 48 for those without any treatment. Incidence is similar to the general population in the US during this period. Patients with treatments and comorbidities were most likely to be hospitalized with COVID-19.
M. Dewigne et al. Low incidence of COVID-19 in hidradenitis suppurative: how to interpret it? P064
In Belgium, a prospective monocentric study showed that 5.9% (8 out of 135) of the HS patients developed mild COVID-19 symptoms. The use of biologics like anti-TNF alpha or anti-IL12/23 did not seem to have an impact. The prevalence is here similar to the previous poster by Horvath et al in the Netherlands. Comorbidities were not associated with a higher risk of COVID-19 as opposed to the data from the US (Kopytev et al)
RD. Caposiena Caro et al. May COVID-19 infection induce a paradoxical improvement of a non-responsive case of hidradenitis suppurativa? P161
An interesting case of improvement of HS after COVID-19 infection has been reported by Italian dermatologists in a woman with Hurley III stage disease and that was treated by adalimumab before infection. It is possible the cytokine storm during COVID-19 infection may have reset balance. Of note the patient presents also signs of long COVID.
Report written by Dr. Nicolas Kluger
G. Pappa, et al Evaluation of resorcinol 10% in the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa Hurley I stage: a randomized prospective open study S05-01
Resorcinol is structurally and chemically related to phenol. It displays keratolytic, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. Its use has been poorly described in HS, mainly in the treatment of acute flares. A Greek randomized prospective study aimed to evaluate the effect of local resorcinol 10% in mild disease of HS. Sixty adult patients were included in 3 groups, A with resorcinol 10% cream twice daily, B topical clindamycin 1% twice daily and C a control group. They were evaluated at weeks 4, 12 and 24. The local lesion count was significantly diminished in the group A, and notable already at week 4. The IHS4 score was also significantly improved in the group A compared to clindamycin and controls. The DLQI score was also significantly improved at wks 4, 12 and 24. Self-reported flares were significantly decreased in both treated groups compared to controls (which worsened with time). Adverse events were mild with brown discoloration of the skin (11%), irritation (25%) and desquamation (37%).
Resorcinol could represent an effective and safe therapeutic approach for long-term management of mild HS.
Report written by Dr. Nicolas Kluger
K. Tsiogka, et al. Efficacy of subantimicrobial, modified-release doxycycline compared to regular-release doxycycline for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. S05-03
Tetracyclines are widely used during HS. They have an antimicrobial activity, but also can affect inflammation, proteolysis, angiogenesis, apoptosis and bone metabolism. Their anti-inflammatory activity relies on the inhibition of multiple cytokines et des proteinases (IL-1, --6, -8, TNF-a, MMP-8, -9, and 13). Modified-released doxycycline is available on the market for rosacea. It includes 30 mg immediate-release and 10 mg delayed-release beads. It is anti-inflammatory activity is stronger than this anti-microbial activity. It could lead to less antibiotic resistance and lower adverse events.
Another Greek study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of such doxycycline (M-Dc) compared to regular doxycycline (R-Dc) in adult patients with HS (at any Hurley stage) for three months.
49 patients were included (25 M-Dc, 24 R-Dc). Groups were balanced regarding epidemiologic data, comorbidities and previous therapies for HS.
IHS4 diminished in both groups significantly and DLQI improved at week 12. Clinical response was not found to be significantly associated with any of the baseline factors. Tolerance was good. Three months course of M-Dc showed a comparable response than R-Dc. Modified doxycycline could be used as an alternative to doxycycline with the benefits of less antibiotic resistance.
Report written by Dr. Nicolas Kluger
F. Tsatsou et al. Biosimilar effectiveness in hidradenitis suppurativa patients previously treated with reference adalimumab. P65
Biosimilars are biologic medical products, structurally almost identical to an already approved reference biologic. Despite minor differences in clinically inactive components, biosimilars and reference drugs are identical in terms of safety, purity and potency.
An interesting poster from Greece reviewed 20 patients with moderate to severe HS that were receiving reference adalimumab for > 24 months. Those patients suffered multiple relapses under treatment including progression to new anatomical areas. Patients were switched to one of the biosimilar available in Greece. Patients experiences fewer relapses, less painful and shorter duration of the disease during the follow-up (3,6,9 and 12 months). These results are interesting and biosimilars should not be discarded in case of failure of the reference biologic. However, the poster did not provide now much data regarding the patient's characteristics under treatment as such.
Report written by Dr. Nicolas Kluger
F. Alfageme, et al. Drug survival of Adalimumab biosimilar and Adalimumab originator in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa: A retrospective single centre cohort of 80 patients. S03-03
A retrospective study from Spain that included 80 patients with moderate to severe HS that were biologic naïve received either reference adalimumab (ADA-O, 44) or a biosimilar (ADA-BIO, 36). The authors found a difference in terms of drug survival between both groups with a better survival for the reference for ADA-O. The patient with ADA-BIO (Imraldi) were twice more likely to discontinue treatment than patients with ADA-O. The main reasons were ineffectiveness and side-effets. After stratification,ineffectiveness was more frequent for ADA-BIO than ADA-O (53% vs 24%). The assumption of equal effectiveness of biosimilar are based on non-inferiority studies in psoriasis. However, no studies for all indications are required for their use in other indications. However, a temporal bias is possible as patients that received ADA-BIO received them (since 2020) after patients with ADA-O (since 2016). This result needs to be confirmed or informed by larger comparative prospective studies, in head to head trials.
Report written by Dr. Nicolas Kluger
E. Taudorf et al. Rapid reduction of inflammation in severe hidradenitis suppurativa following treatment with the PDE4-inhibitor Orismilast. S05-05
Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) is upregulated in inflammation and its inhibition may have an impact on T-cells, NK-cells, dendritic cells, monocytes and macrophages. It downregulated inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-a, IFN-g, IL-8, IL-7 and IL-23.
OSIRIS is a Danish phase 2A, monocentric. prospective open-label and single-arm study that evaluated the efficacy of an oral PDE4-inhibitor Orismilast twice daily for 16 weeks in 24 patients with HS. However, the communication revolved only about one of the patients included in the study, a 34 yo male with a severe disease. The impact notable on swelling and pain. However, there were minimal objective changes in the mutilated skin areas. It is necessary to wait for the full study to make a better idea of the efficacy of this treatment.
Report written by Dr. Nicolas Kluger
K. Dudink, et al. Guselkumab for hidradenitis suppurativa: a phase II open label, mode of action study. S05-7
The aim of this monocentric phase II study was to evaluate the safety, tolerability, efficacy, and mode of action of guselkumab, which is an anti-IL23 monoclonal antibody, in moderate to severe HS. Guselkumab was administered at week 0, 4, 8 and 12 and clinical response was evaluated at wk 16. The primary objective was to analyze the changes in inflammatory pathways induced by guslkumab in HS skin lesions at week 16. The secondary objectives with the efficacy, short term safety and tolerability. The patients that could be included were adults with a recent HS of less than a year with a moderate to severe HS and 2 anatomical locations or more at base line. Twenty patients completed the study with a notable efficacy, guselkumab induced a response in 65% of the patients. Guselkumab modulated gene expression of HS associated cytokines. This study needs to be confirmed on larger groups.
Report written by Dr. Nicolas Kluger
A. Ezanno et al, Impact of surgery in hidradenitis suppurativa: results of a prospective French multicenter study. S05-08
Anne Ezanno presented the preliminary result of a French multicentric prospective study regarding the impact of surgery in HS. Both patients and surgeons had to answer to questionnaires. For patients before surgery, included, smoking, pain, the impact of the lesion. For surgeons before surgery, data included information about the patient’s HS and the surgery approach including anesthesia etc. Questionnaires were filled again by the patients and surgeons at 1 and 6 months.
During the communication, only the results from the patients’ side is reported.
91 patients were included. Delay between HS diagnosis and first surgical consultation for wide excision was of 12 years. 74% had long-term antibiotics and 19% biologics. Surgical excision in HS was indicated at all stages of the disease. Mean time of wound healing was 69 days. Pain dropped from 5/10 to 2.4/10 at one month, and 1.5/10 at 6 months after surgery, while the DLQI dropped from 15 before to 12.8 and 6.6 at one and 6 months after.
Report written by Dr. Nicolas Kluger
Pregnancies during HS: what is known from the literature?
A Molina-Leyva et al. Hidradenitis suppurativa and pregnancy: a systematic review. P027
The systemic review of articles from 2015 to 2021 was performed by Spanish authors. They identified 46 articles, and reviewed after selection on 7. The results of six questions are summarizes in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Questions related to pregnancy during HS
Keratosis pilaris and HS: a new association?
F. Purcell et al. The co-occurrence of keratosis pilaris and hidradenitis suppurativa. P126
Keratosis pilaris is a genetic disorder of follicular hyperkeratinization. An observational descriptive study from Denmark reviewed 62 patients with HS. Almost 73% patients were women, with a mean BMI of 34 and Hurley stage II in two third of the cases. The frequency of keratosis pilaris was 82%. The most prevalent areas with KP were the extensor surfaces of the arms and the thighs. Further studies are necessary to evaluate the relevance of this association in this small series.
Kinase inhibitors as a cause of HS
E. Molina Figuera, et al. Sorafenib-induced hidradenitis suppurativa: A case report. P145
N. Cosgrave, et al. Sunitinib – induced hidradenitis suppurativa in a patient with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: mechanistic insights P171
Two posters reminded that multiple kinase inhibitors (VEGFR, PDGFR, RAF kinases) used in oncology such as sorafenib and sunitinib can be responsible for HS lesions.




